March is AED Maintenance Month!
Maintaining your defibrillator is as important as having one
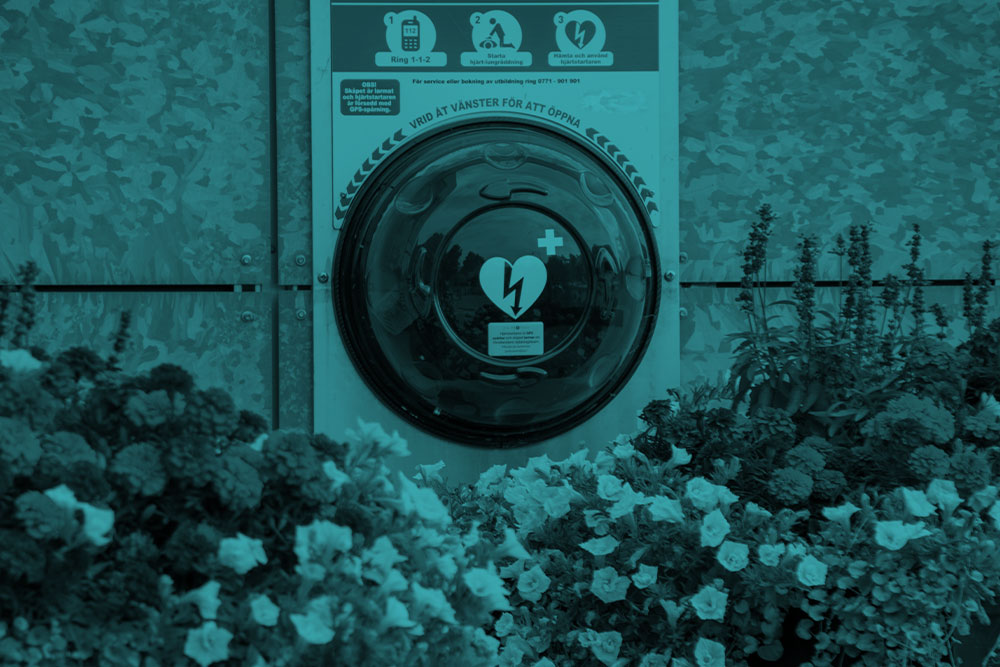
With the survival rate of sudden cardiac arrest being below 10%, the emphasis to have Automatic External Defibrillators (AEDs) in all places where we live, work, and play is becoming increasingly important. It is equally important to remember that having a maintenance plan in place will ensure all AEDs are ready to help save a life when and if needed. When a defibrillator is deployed during an emergency, it is crucial the AED is ready to be used. The outcome for the patient could be even more devastating if the AED was available but not functioning properly.
Proper maintenance of the AED is essential to ensure that it works correctly when needed. Here are some tips on how to maintain an AED:
Read the user manual: To maintain properly functioning AED, read the manual thoroughly. This will help you understand the device’s functions and how to use it correctly. It will also get you familiar with the manufacturer name when needing to reorder the disposables such as batteries & pads.
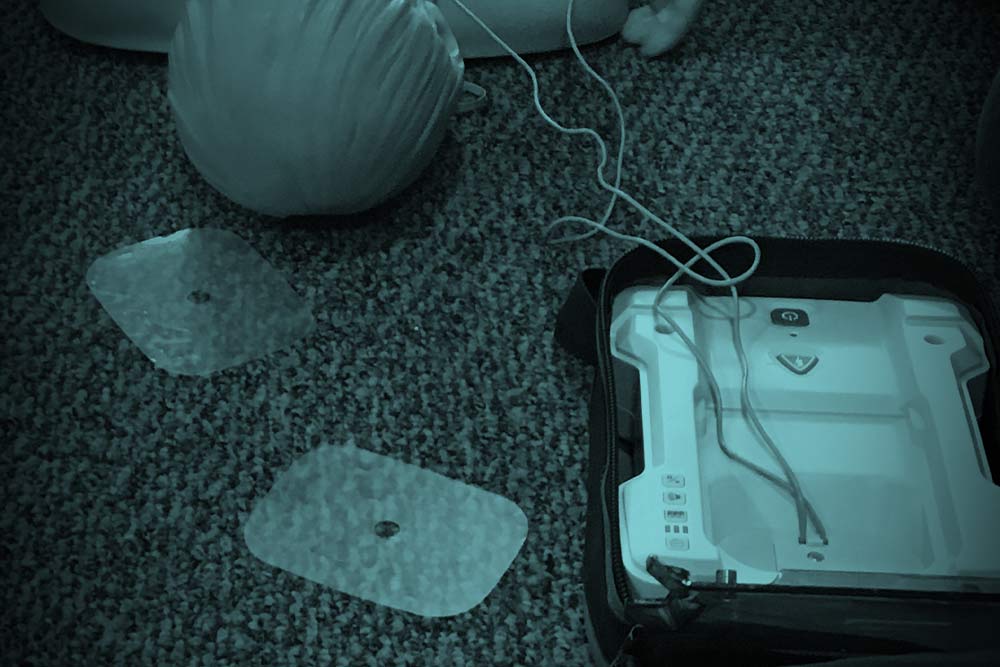
Regularly check the battery and electrode pads: Check the AEDs battery and electrode pads regularly. Replace them immediately if they are expired, damaged, or low on charge.
Perform self-tests: AEDs have a self-test feature that checks the device’s internal components and battery charge. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for performing regular self-tests.
Keep the AED clean: Wipe the AED with a clean, dry cloth to remove dirt, dust, or debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents that can damage the device.
Store the AED correctly: Store the AED in a dry, cool place. Avoid exposing the device to extreme temperatures or moisture as may inhibit the AED’s performance.
Keep the AED accessible: Place the AED in an easily accessible location that is visible and known to everyone. Ensure that it is not ever blocked by any obstructions, so it is clearly available when an emergency arises.
Train your staff: Ensure that your staff is trained in AED use and maintenance. Regular training can help them respond quickly and confidently in an emergency. Ensure it is part of the onboarding process when a new team member comes on board. You should also appoint someone to carry out monthly checks and have these checks logged.
Below is a checklist when doing an AED Maintenance check:
• Is the Active Status Indicator light on your AED flashing green?
• Are the AED pads plugged in and ready for use?
• Does the AED appear to be undamaged and ready for use?
• Is the AED free of chirping and warning notifications?
• Are the AED pads within their usable date?
• Is the AED battery within its usable date?
If the answer to any of these questions is no, call Customer Service/AED manufacturer to determine what the issue might be with the AED.
By following these tips, you can maintain your AED in good condition and ensure that it is always ready to use when needed.
References;
Maintaining your defib is as Important as having one – Eiremed.ie
Guide to Defibrillator Maintenance and upkeep | St John Ambulance (sja.org.uk)
How To Maintain Your AED | AED Defibrillator Maintenance (defibtech.com)